6.1 Welding Overview
Welding is the common process of joining materials through melting and fusion, and inspection of structural welds in metals is the single most common application for ultrasonic flaw detection. Welding can be done by means of several methods including electric arcs, gas flames, and lasers, but for ultrasonic testing the geometry of a weld rather than how it was made is the primary concern. This section focuses on common construction welds typically used to join pipes, plates, and metal structures.
Welding overview
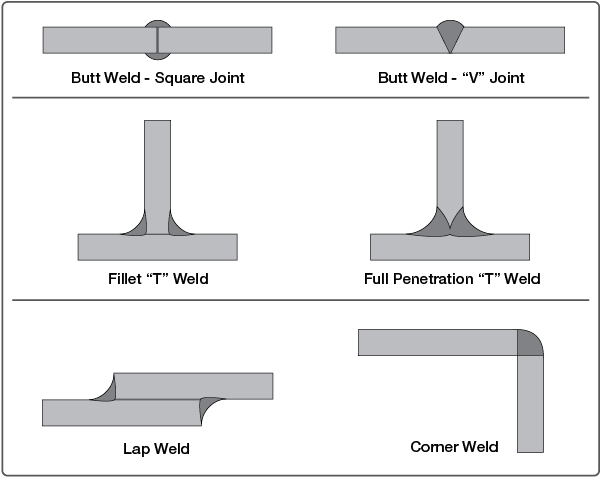
There are a potentially large number of possible weld geometries, but those commonly inspected by ultrasonic techniques fall into four basic categories as seen below.
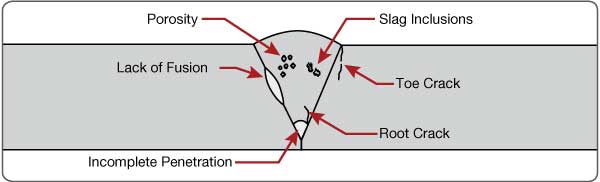
The most commonly encountered flaws types are cracking, lack of fusion, incomplete penetration, porosity, and slag inclusions. All of these are potentially detectable through ultrasonic testing.