1. Application
Gray-scale masks is a technology used to fabricate molds for complex-shaped micro lenses or other products that are comprised of high-quality 3D microstructures. The gray-scale mask is used for 3D patterning; a resist coating is irradiated with a multiple-gradation laser to create the 3D pattern (Figure 1). Measuring the 3D shape of the resist after irradiation is essential for quality control. Since the 3D pattern is easily damaged, noncontact measurement is required to verify its integrity.
2. Olympus' solution
Olympus' LEXT 3D laser scanning microscope enables noncontact, three-dimensional imaging of the concave or convex shape of a gray-scale mask with high resolution and high contrast. Thanks to objective lenses with high numerical apertures and an optical system designed to obtain maximum performance from the 405 nm laser, the LEXT microscope can capture the profile of irregular slopes accurately, leading to reproducible, reliable 3D profiles (Figure 1). In addition to measuring the shape of samples, users can also clearly visualize minor irregularities using laser differential interference.
| Concave pattern | ||
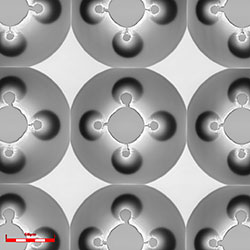 Objective lens: 50x 50X, Zoom 1x |  Objective lens: 50x 50X, Zoom 1x | 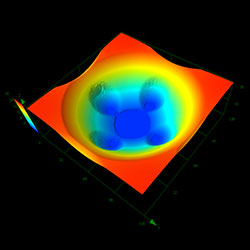 Objective lens: 100x 100X, Zoom 1x |
| Convex pattern | ||
 Objective lens: 50x 50X, Zoom 1x | 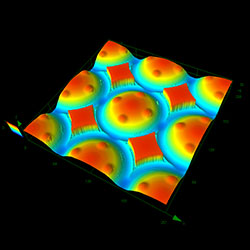 Objective lens: 50x 50X, Zoom 1x | 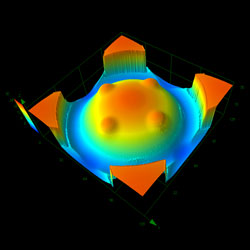 Objective lens: 100x 100X, Zoom 1x |
Figure 1. Imaging concave and convex patterns using the LEXT microscope
Figure 2. The lens fabrication process using a gray-scale mask.
Step 1
- Resist coating

Apply resist onto the glass.
- Drawing (laser irradiation)

Irradiate the resist with a multiple-scale laser beam to create a positive resist.
The irradiated area is exposed and softened.
- Soak in the developer

Develop the resist and strip away unnecessary regions. 3D profile evaluation during this phase is key to quality management.
Step 2
- Electroplating

Apply plating to the resist.
- Etching

Dissolve the resist through etching and flip the plating over to complete the original (metal mold).
Step 3
- Use thermo-compression to bond the film to the metal mold.
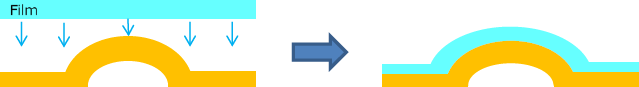
- Imprint

Peel the film off the metal mold and flip it over.
- Resin molding
Pour resin into the film.
- Finish

Solidify the resin and remove it from the film mold to complete the lens.