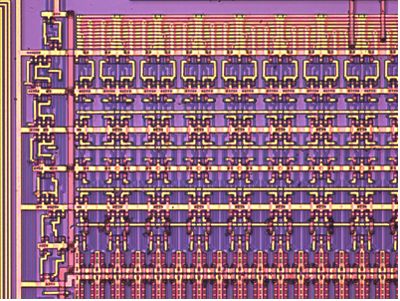
Reflected Brightfield Observation
It is to observe the light reflected directly from specimen.
The light from the illumination lamp is vertically guided through objectives and incident on the specimen. The light reflected from the specimen is observed through the objective.
Silicon Wafer
Koehler Illumination
Light from the primary light source is collected by the collector lens and forms an image at the AS (aperture stop) position. This image acts as a secondary light source, reproducing the image at the objective's exit pupil position and casting telecentric (parallel light) illumination on the
specimen surface. This is generally known as "Koehler Illumination" and has two main features. One is its brightness and uniformity; the other is that it allows both AS and FS (field stop) settings to be changed independently.
The Effect of FS
FS settings adjust the field of view at the extreme periphery and prevent extraneous reflected light from altering the forming light. This effectively eliminates flares from the whole image.
The Effect of AS
AS is effective when adjusting the illumination N.A. or changing the image contrast. Generally, the best contrast is obtained by diapharagming the objective pupil diameter to about 80%. However, when using objectives of over 100x magnification, better contrast images are obtained by
diapharagming the objective pupil diameter to less than 50%.
Related Link
> Top of Digital Microscope page