Strehl Ratio
When a point light source is observed, an aplanatic optical system concentrates a light beam into one point at the image location. Contrarily, an optical system with aberration does not concentrate the beam into a point, resulting in a divergence.
Figure 1 shows the appearances of a point image (intensity distribution of a point image) in both optical systems.
Figure 1: Light Convergence Appearance (Point Image Intensity Distribution) in the Image Field 
Assuming a convergence ratio in the image field of an aplanatic optical system (light intensity converging on an airy disc) as 100%, the convergence ratio in an optical system with an aberration is referred to as a "Strehl Ratio (SR)". As shown in the graph in Figure 2, an optical system with a higher SR value is closer to an aplanatic optical system.
Figure 2: Strehl Ratio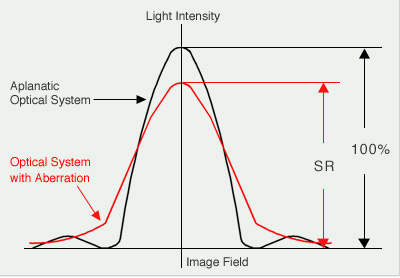
A Strehl ratio of 80% is commonly known as the diffraction limit. An objective lens below this limit is not assumed to have satisfactory performance. An objective lens with a Strehl ratio of more than 95% compares favorably with an aplanatic lens in performance for common observations.
Note: A laser interferometer is used for actual optical performance evaluations, thus providing evaluation with a single wavelength.
Unless otherwise noted, Olympus offers Strehl ratio values measured with the e-line laser (544nm).
Related Link
> Top of Digital Microscope page