Several techniques can be used to eliminate or reduce the edge effect that affects or even prevents the inspection on areas close to edges, fastener heads, etc.
1. Shielding
Shielding is the most often used technique to avoid edge effect. Ferrite is the best material used and reduces the sensitive area to the
internal diameter of the shield. At lower frequencies the eddy currents will propagate slightly beyond the shield diameter.
2. Differential Coils
The use of differential coils can be helpful to avoid external interference such as edge effect. With the coils aligned to keep the same distance to the edge, it is possible to inspect sometimes even with an overlap.
3. Maintaining a Constant Distance
By using a guide it is possible to keep a constant distance to an edge or another object such as a fastener head (see Figure 1 and 2).

Figure 1
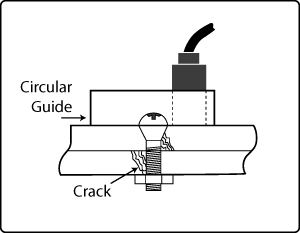
Figure 2
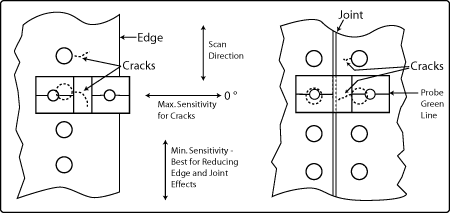
Figure 3
4. Using Directional Probes
Directional probes can be useful as their sensitivity at 90° is very low. The reflection sliding probes with transparent lenses are the best examples of this (see Figure 3). Because of low sensitivity at 90° they ignore edges and joints between two plates or skins. A straight edge can be useful as a guide (see Figure 4).
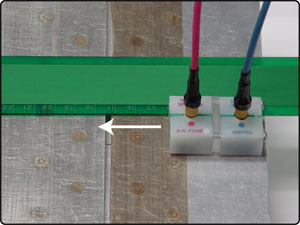
Figure 4
5. Using Directional Probes Across the Edge or Joint
The signal produced by the joint or edge can often be differentiated from the defect (see Figure 5).
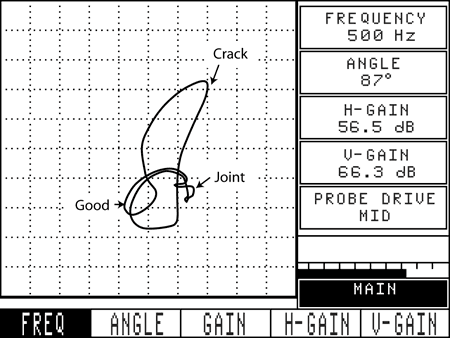
Figure 5
6. Adding Another Piece of Similar Type Metal to Probe
By adding a piece of similar type metal to the probe, it is possible to establish a path for the eddy currents and sometimes use it as a guide as well (see Figure 6).
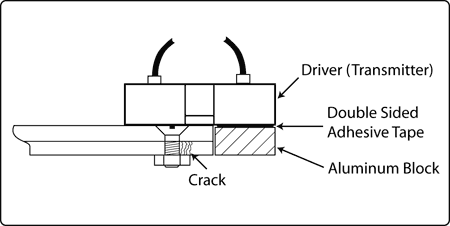
Figure 6