Beautiful, lustrous pearls have always been an attractive raw material in the jewelry industry. However, the value of this kind of biological specimen from the natural environment varies greatly depending on the pearl type, authenticity, and characteristics such as size, color, shape, luster, and surface.
One of the top concerns regarding value is whether the specimen is a saltwater or a freshwater pearl. Saltwater pearls, also known as seawater pearls, are generally more valuable than freshwater pearls due to their rarity, luster, and quality. Freshwater pearls, while beautiful, are more abundant and typically less expensive.
Adding to this concern is the authenticity—whether it is a natural or imitation pearl. Real pearls command high prices due to their organic formation, unique characteristics, and market demand, while imitation pearls are primarily valued for their aesthetic appeal at affordable prices.
So, how can the type and authenticity of pearls be identified effectively?
The Increasing Difficulty of Identifying Authentic Pearls
In the past, freshwater and saltwater pearls could be distinguished by their appearance. However, the improvement of modern imitation technology and the continuous improvement of fake pearl jewelry have added a certain degree of difficulty to the identification of pearls. In most cases, it’s difficult to distinguish them merely by observing with the naked eye.
The type of pearls can no longer be accurately determined using traditional methods such as appearance, temperature, and touch. This means that we need more reliable identification methods to determine the type and authenticity of pearls.
Easily Identifying Pearls with XRF Technology
Portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology can provide good technical support for pearl identification without damaging the pearl. XRF uses X-rays to analyze and detect the chemical elements contained in different types of pearls. By knowing the elemental composition of saltwater and freshwater pearl types, you can match the results to the pearl type to instantly identify it.
Consider the following example. By testing pearl samples using a Vanta™ handheld XRF analyzer, we find that saltwater pearls generally have higher levels of strontium (Sr) and almost no manganese (Mn). In contrast, high levels of manganese (Mn) and low levels of strontium (Sr) are detected in freshwater pearls.
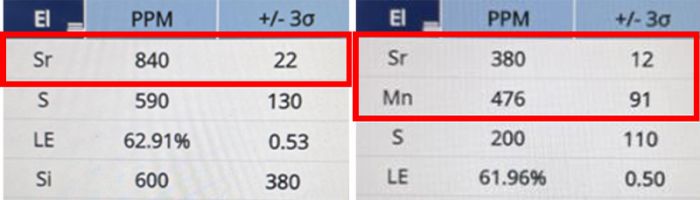 |
Vanta analyzer results for saltwater pearls (left) vs. freshwater pearls (right).
Portable XRF technology is also useful for identifying real pearls from fake pearls. Natural pearls are mainly made of calcium carbonate. In contrast, fake pearls are commonly made of glass or resin.
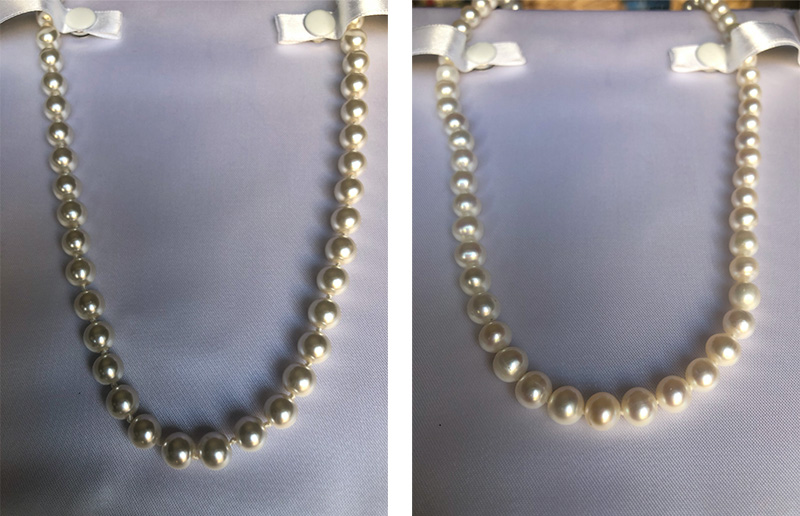 |
Real pearls (left) vs. fake pearls (right).
Using XRF results, you can quickly identify natural pearls from imitation pearls by verifying whether the pearls contain mostly calcium carbonate. Read more about this process in our post, Shining Like a Diamond or Rhinestone: Identifying Precious Gems with XRF Analyzers.
Accuracy and Efficiency in XRF Results for Pearl Identification
The Vanta analyzer’s Geochem mode can be used for pearl identification to meet stringent requirements in terms of accuracy. The detection efficiency is increased 5 to 10 times compared to traditional laboratory methods.
The Vanta series comes in handheld XRF analyzers and benchtop XRF analyzers built for the showroom so you can easily get results on the spot. If you have any questions about pearl identification with XRF, reach out to our team of specialists for a demo.
Related Content
Comparing Gold Testing Methods to Maximize Profits: XRF vs. Acid Scratch vs. Conductivity Testing
Plug-In Scripts Enhance Your XRF Data Display: Example in Watch Authentication
5 Reasons to Test Jewelry with the Vanta™ GX Precious Metal Analyzer


