激光显微镜解决方案
►Feature of a laser microscope
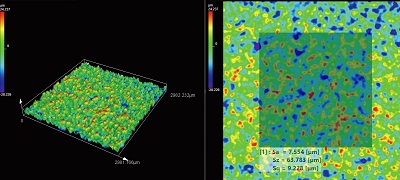
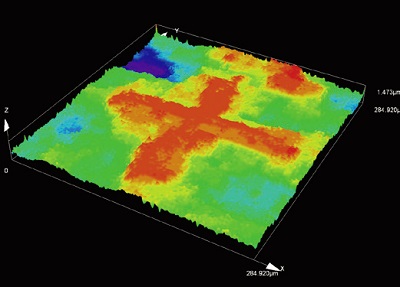
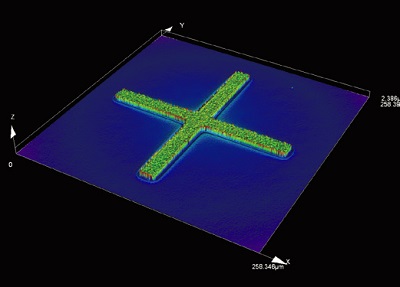
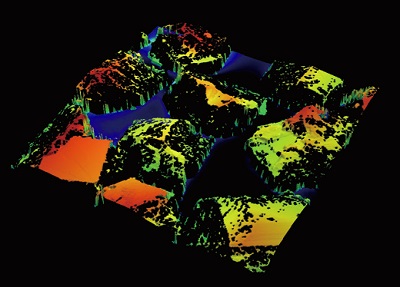
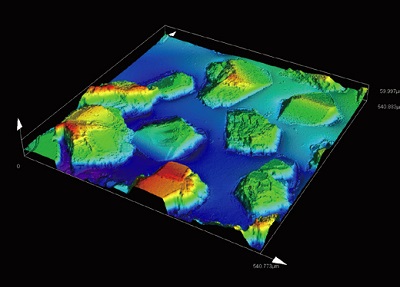
1. Sub-micron 3D observation/ measurement
| Observe steps in the nanometer range and measure height differences at the sub-micron level. |
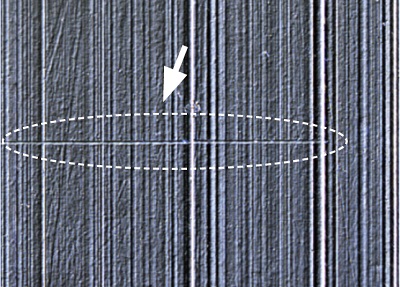
2. ISO25178-compliant surface roughness measurement
| Measure surface roughness from linear to planar. |
3. Non-contact, nondestructive, and fast
| No sample preparation required—simply place the sample on the stage and you're ready to measure. |
►Advantages of a laser microscope
Conventional measuring tools | Laser microscope | |
Optical microscope, digital microscope | ||
•Unable to measure small shapes •Poor lateral resolution •Non-traceable measurement results |
| •Precision 3D measurement •0.12 μm lateral resolution •Traceable measurement results |
Stylus surface roughness tester | ||
•Can damage the sample’s surface •Information from only one line •Difficult to place the stylus on a target position |
| •Non-contact measurement doesn’t damage the sample •Acquire information from an entire plane •Pinpoint measurement |
White light interferometer | ||
•Has difficulty capturing rough surface shapes •Poor lateral resolution makes positioning difficult •Inconvenient inclination adjustment |
| •Accurate rough surface measurement by capturing small slopes •0.12 μm lateral resolution •Just place your sample on the stage to start measurement |
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) | ||
•No color information •Samples must be destroyed and prepared in advance •3D shape measurement is not possible |
| •High-definition color observation •Nondestructive and no sample preparation required •Precise 3D measurement |